Kill The Termite Colony, Target The Termite Queen
June 13, 2025
Termite Ground Treatment for Malaysia Properties
June 16, 2025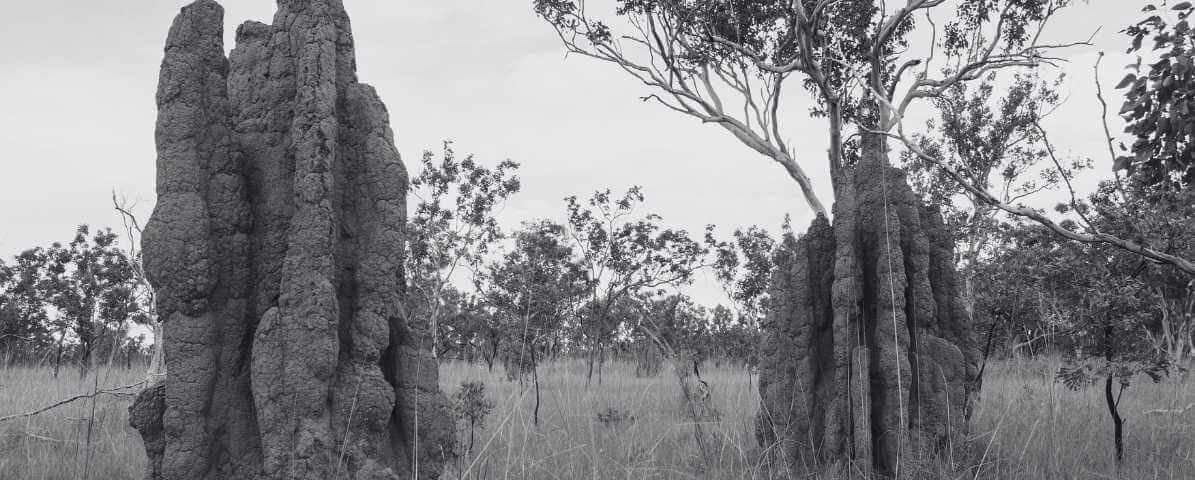
Termites Blog
Recognising the types of termites, their mounds, signs of termite activity, such as small holes in wood, presence of mud tubes or damaged wood. These can help home and business owners take timely action to minimise damage.
Introduction to Termites in Malaysia
The Common Types of Termites Species in Malaysia
Termites are among the most destructive pests affecting residential and commercial structures in Malaysia. With warm, humid climate conducive to termite activity, understanding various types of termites is crucial for effective pest management. Explore the termite species in Malaysia, their habits, signs of infestation and how to combat and prevent termite damage. They are an ever present threat to wooden structures, decaying wood and even soil-based foundations.
The warm, moist environment fosters a thriving ecosystem for them to build colonies underground and above ground. Mud tubes serve as protection, allowing termites to access food sources safely, avoiding exposure to dry air and predators. Understanding the different types of termites, especially the prevalent species like Coptotermes and Coptotermes formosanus, is essential for proper identification, treatment and prevention.
Types of Termites That Are Common in Malaysia
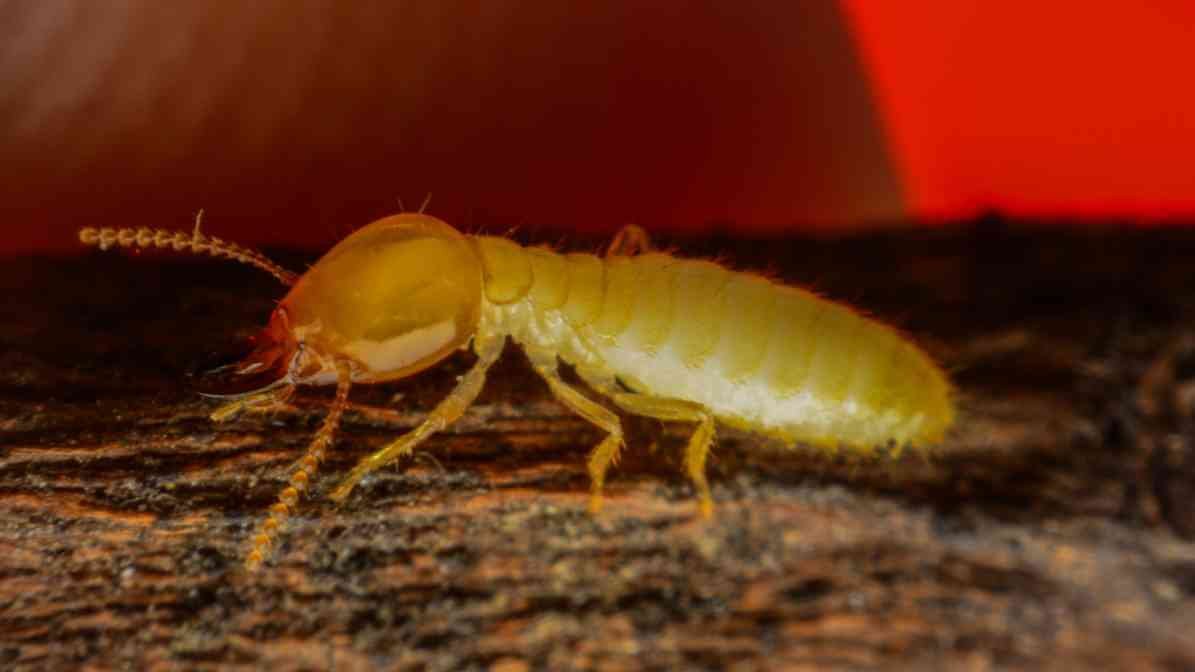
Subterranean Termites (Coptotermes formosanus)
Description and Habitat:
Subterranean termites, especially Coptotermes formosanus, are among the most destructive species in Malaysia. These termites dwell primarily underground, building extensive networks of mud tubes narrow, shelter tubes used for transportation and protection. They travel across soil and surfaces like fence posts and building foundations.
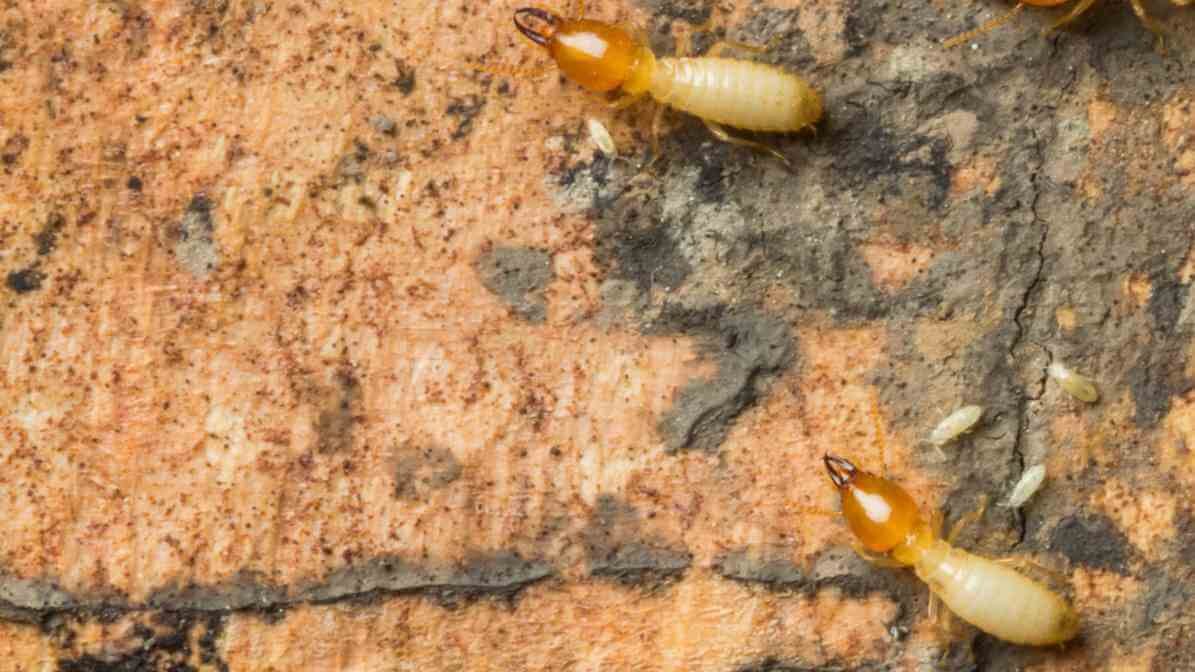



Behaviour:
Formosan subterranean termites are famous for their aggressive nature and large colony sizes. Sometimes with the colony containing millions of workers, soldiers, kings and queens. They build these shelter med tubes to search for food, such as decaying wood or even drywood. And t can form new colonies easily from a founding pair.
Signs of Activity:
Detecting these termites involves noticing mud tubes, small holes in wood or hollowed-out structure and weak spots. Their activity often results in significant termite damage, particularly to wooden structures like support beams and fence posts.
Impact:
The aggressive feeding habits of Coptotermes threaten your property’s stability, especially if dry wood or furniture is infested. Their ability to form new colonies increases the risk of widespread infestation without early detection.
Why Understanding the Types of Termites Matters?
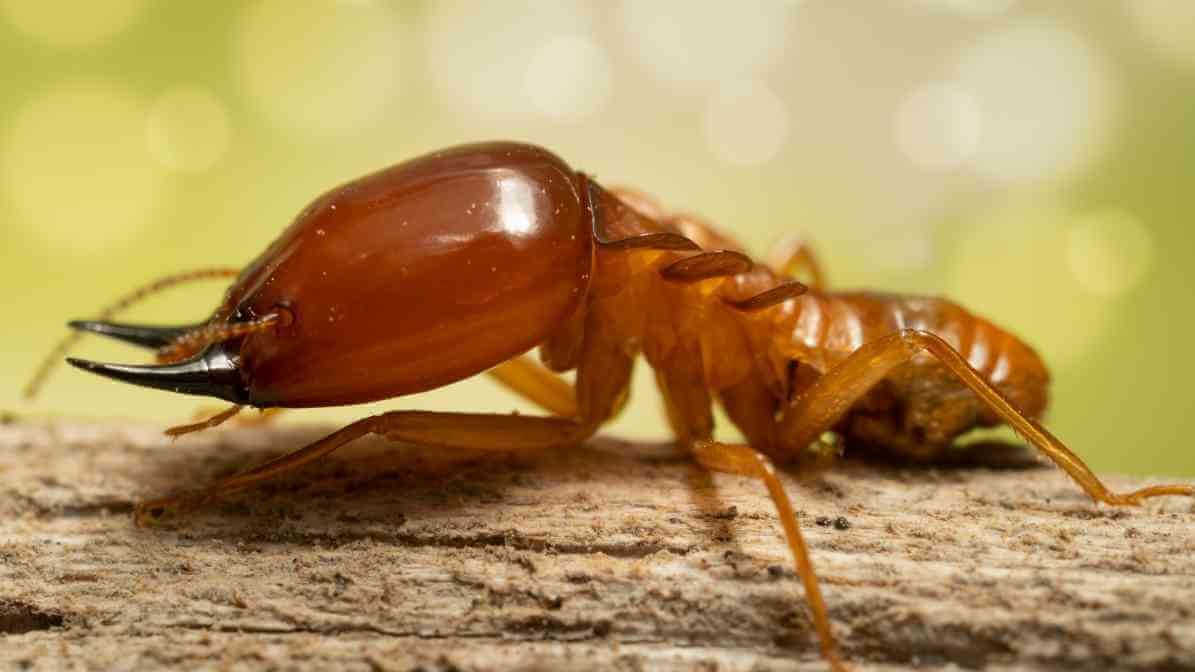
Drywood Termites (Cryptotermes cynocephalus)
Characteristics and Environment:
Unlike subterranean species, drywood termites live within the wood itself. Typically in dry wood with low moisture content, such as furniture, attic beams or window frames. They prefer dry wood environments and do not require contact with soil.
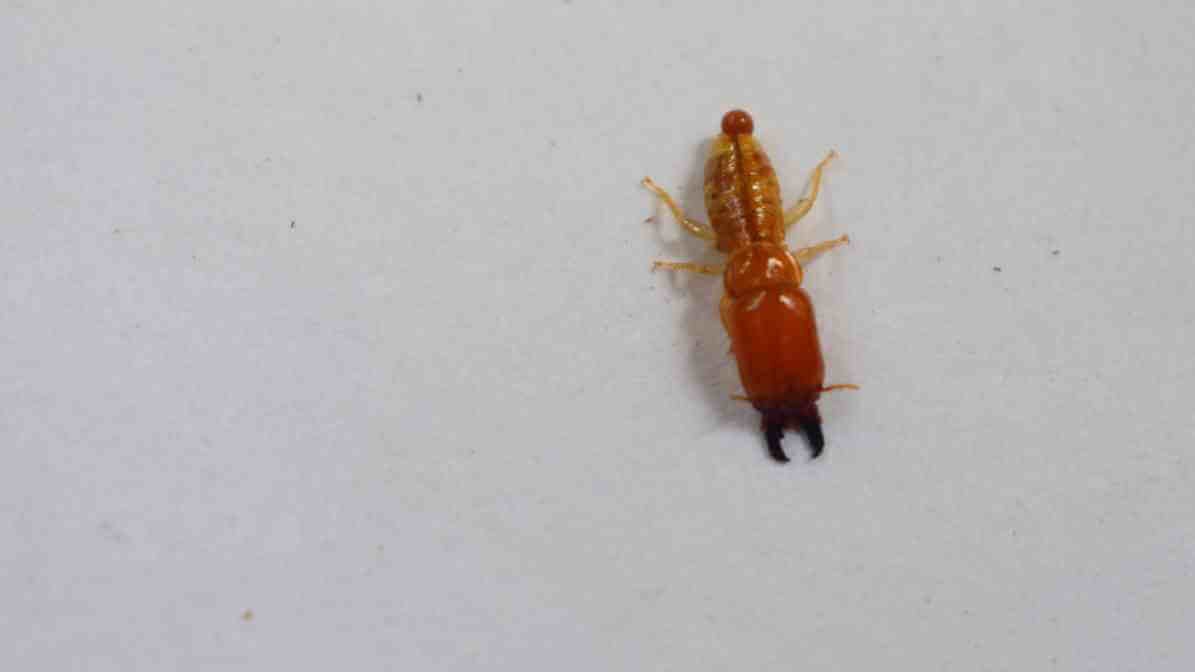



Infestations and Colonies:
These drywood termite colonies usually consist of kings and queens that produce winged swarmers during breeding seasons. The presence of small holes and piles of frass (wood debris) at exit points signals their activity.
Symptoms and Damage:
Signs include drywood termite infestations visible as hollow, weaken wood with small holes. Often accompanied by shelter tubes though less extensive than those of subterranean types. Failure to address drywood termite infestations early leads to termite damage that compromises furniture and structural elements.
Importance of Treatment:
With their behaviour, discreetly living inside wood, termite treatment typically involves fumigation or localised chemical applications. Effectively eliminate drywood termites and protect dry wood furniture from future drywood termite colonies.
Understanding The Types of Termites and Their Habitat
Dampwood Termites (Archotermopsidae)
Overview and Habitat:
Dampwood termites get easily attract to decaying wood with high moisture content. Often in areas where ventilation systems fail or in damp environments. They are less common in built structures but can threaten outdoor wood like fallen logs or old trees.
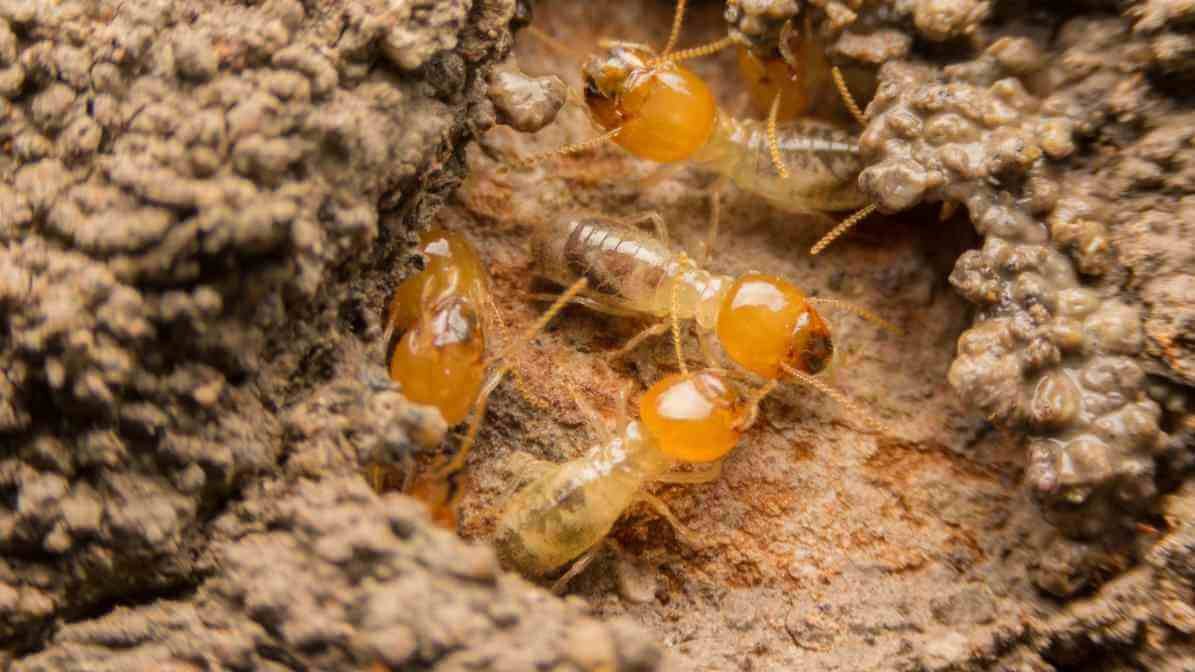
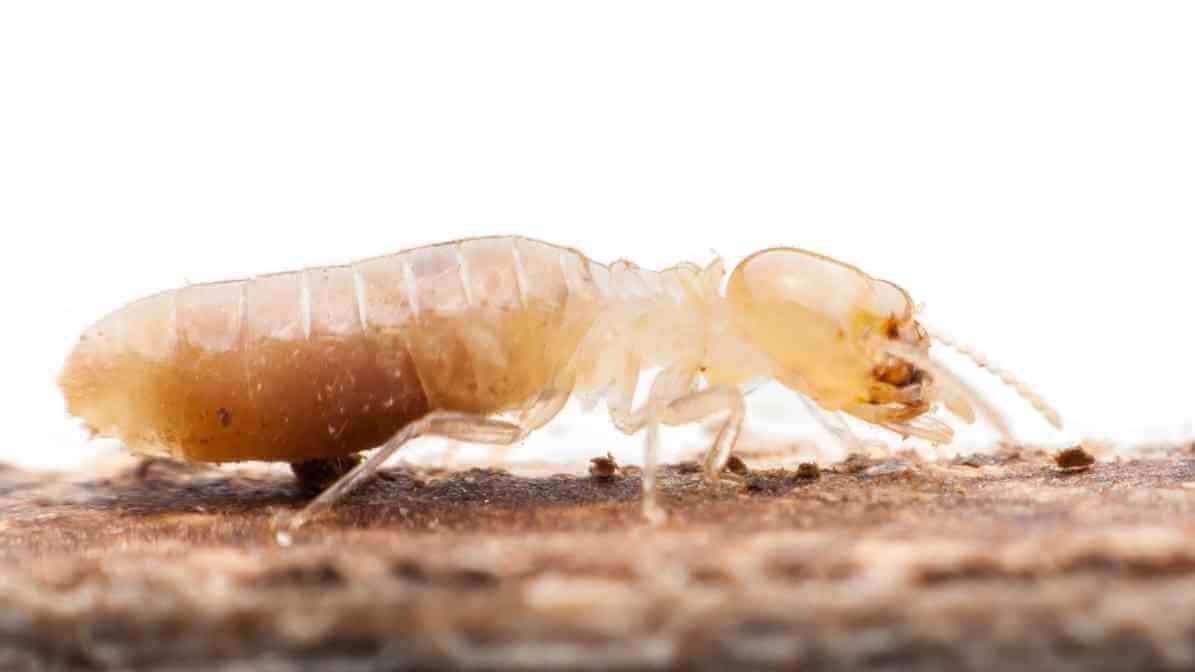
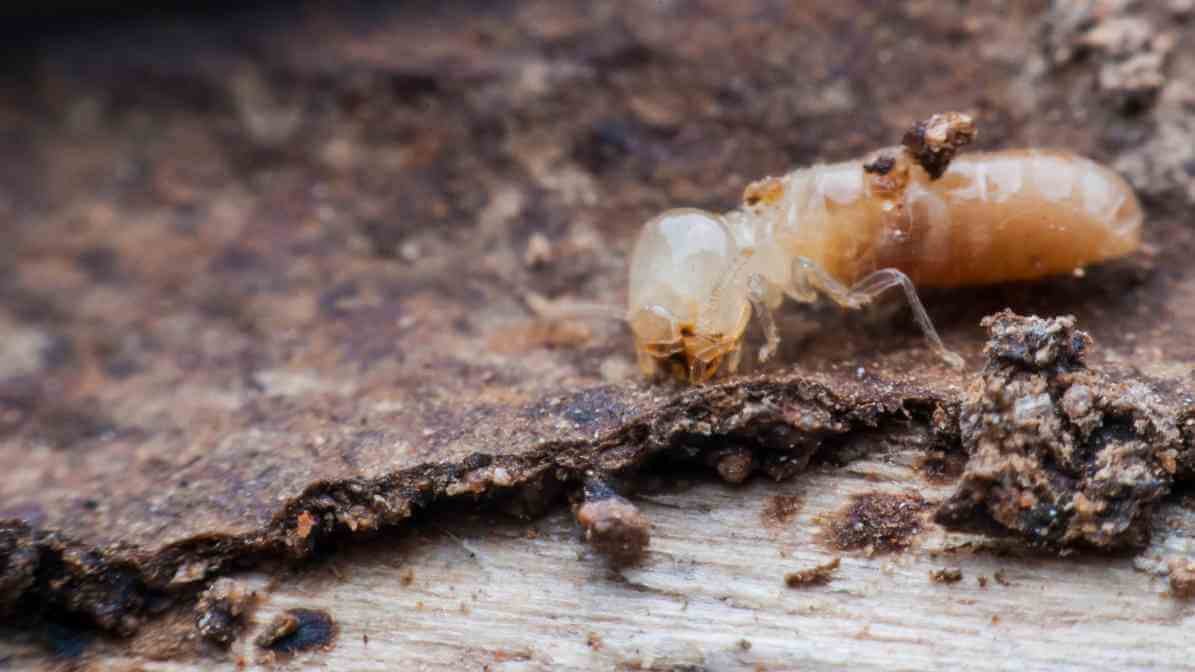



Characteristics:
- Appearance: These termites are small and typically form drywood termite colonies inside the wood they consume.
- Signs of infestation: They leave small holes and produce shelter tubes or small piles of frass (wood debris).
- Habitat: Resides in wooden structures, especially where ventilation systems trap moist air or where wood is decayed.
Role and Effect:
While they play a natural role in decomposing decaying wood. Their presence around properties indicates areas of excess moisture which can invite termites build opportunities. They are generally not a direct threat to wooden structures unless dampwood enters those structures.
Impact:
Drywood termite infestations can silently weaken furniture or structural wood. Leading to termite damage that may go unnoticed until significant.
Do All Types of Termites Build Mud Tubes?
No, only subterranean termites like Coptotermes build mud tubes. Drywood termites tend to remain within the wood, often leaving small holes but not mud tubes.
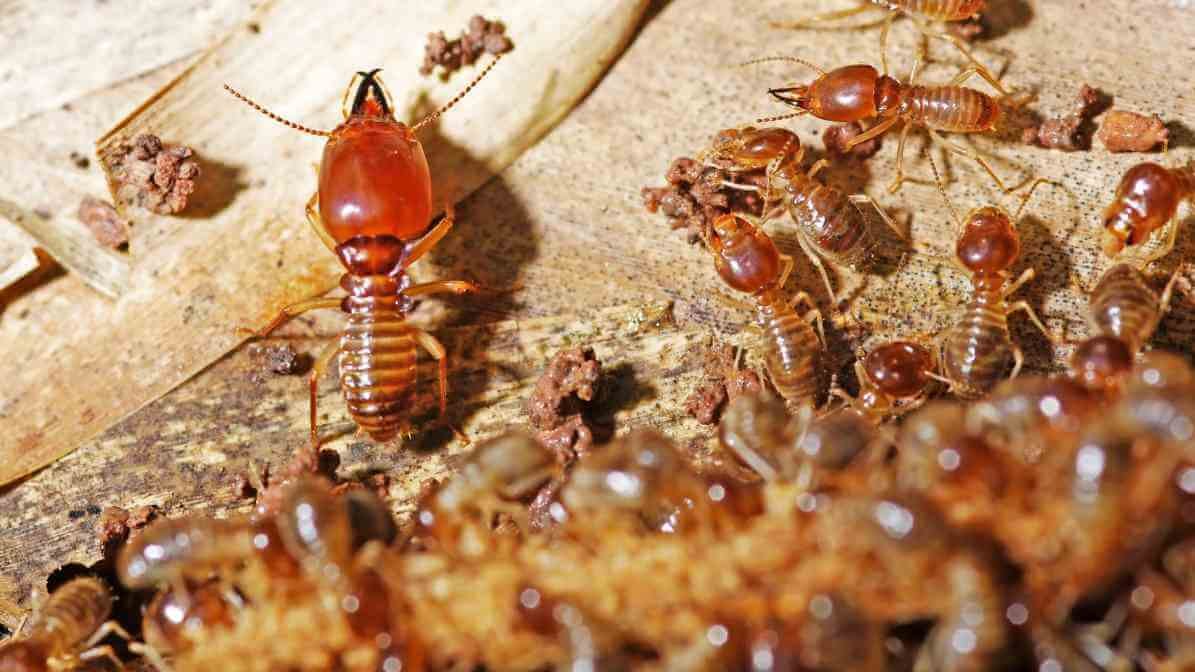
Building Nests in Colonies, Swarmers and Reproduction
Habitats and Behaviours of Various Types of Termites in Malaysia
They build mud tubes and shelter tubes which serve as protective pathways. Allowing workers to search for food such as decaying wood or drywood, while remaining safe from dry air and predators. These tubes often are on the foundation walls, fence posts or buried underground. Small holes in wooden structures indicate active termite activity, as they emerge from their nests or furrows to forage.
Recognising these signs of termite activity early on can help prevent extensive damage. The kings and queens of termite colonies are responsible for reproduction. During certain seasons, especially after rain, swarmers emerge to form new colonies. This process can lead to sudden increases in termite populations around property perimeters, increasing the risk of infestation.
Understanding The Characteristics of Termite Mounds in Malaysia
The Types of Termites Living in The Termite Mound
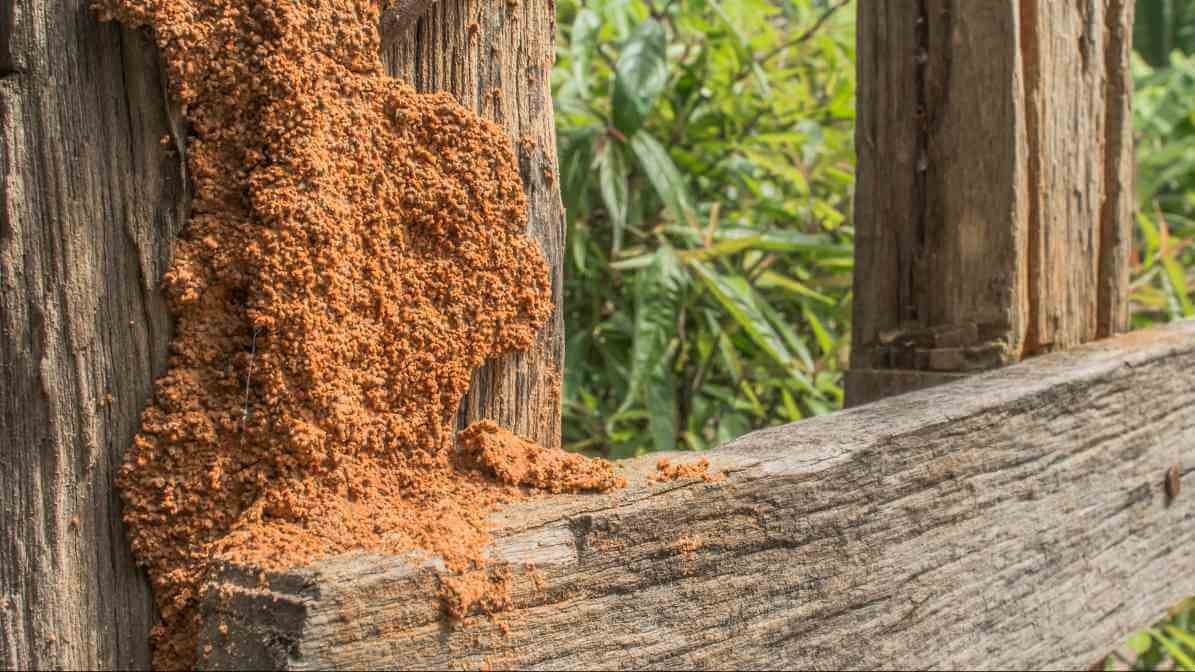
Underground and within wooden structures are common nesting sites for termites, certain species are also construct prominent termite mounds. These structures serve as large, intricate colonies that can be in fields, gardens and forests across the country. Although not all termite species build mounds, those that do are usually reticulitermes or macrotermes.
Size and Shape
Malaysian termite mounds can vary widely in size, from small heap-like formations to towering structures several meters tall. The shape often reflects the species and environmental conditions, with mounds designed to regulate temperature and humidity.
Materials
Constructed from soil, saliva, and termite faeces, these mounds provide a stable environment with optimal conditions for their colonies.
Design Purpose
The mound's design facilitates air circulation. With natural ventilation systems that maintain favourable temperature and fresh air inside, essential for the survival of the colony.
Impact on Structures and Agriculture
Types of Termites, The Function and Ecological Role
Termite mounds are more than just homes. They play significant roles in the ecosystem by aiding soil aeration and nutrient cycling. However, in urban or agricultural settings, they can sometimes cause problems when located near buildings or farmland. While termite mounds generally do not threaten wooden structures directly, their presence indicates active termite colonies nearby.
If these mounds are close to your property, there's a higher chance that subterranean termites. Especially Coptotermes, they can invade properties through the ground. Especially if the mounds are connect to underground tunnels.
Signs of activity around or near mounds include fresh soil deposits or damaged plants.
Management involves careful inspection and, if necessary, professional termite treatment to eliminate underlying colonies before they invade structures.
In some cases, fence posts and foundations. They can be protect by installing physical or chemical barriers to prevent termites from reaching your property.
Impact of Termites on Structures
Damages Common Types of Termites Pose Onto Building Structures
Subterranean termites, like Coptotermes and Coptotermes formosanus, are notorious for causing significant termite damage to wooden structures, fences, and even the foundation of buildings. They often attack fence posts, support beams, and drywood termite colonies within furniture or framing.
Their ability to create new colonies from one queen or a pair of reproductive termites helps them grow quickly. Making it harder to control them over time without the proper knowledge. Damage caused by termites often appears as hollowed-out wood, small holes or weakened structural integrity posing safety risks.
Controlling and Preventing Termites in Malaysia
Types of Termites Treatment Options Available
Effective termite treatment strategies depend on the species involved and the extent of infestation. Common approaches include:
Applying termiticides in the soil around the structure's perimeter. This method helps to create a chemical barrier that terminates termites attempting to access the building.
Installing bait stations both above and below ground to attract termites, especially workers soldiers. These baits contain poison that gradually eliminates entire colonies.
Fumigation
For severe drywood termite infestations. Fumigation with gases like sulfuryl fluoride can eradicate drywood termite colonies within furniture or structures.
Physical Barriers
Using metal or sand barriers during construction helps prevent termite intrusion.
Professional Termites Control Services
Innovative Pest Blog Summary
In Malaysia, understanding the common types of termites, especially Coptotermes, Coptotermes formosanus and drywood termites. Is fundamental to effective pest management. By recognising their habitats, behaviours and signs of infestation, property owners can implement targeted termite treatment and prevention methods. Regular inspections, good maintenance practice and professional intervention form the cornerstone of minimising termite damage.
Termite control helps protects wooden structures, support beams, fence posts and other vulnerable elements. Being vigilant about small holes, shelter tubes and mud tubes can save you from extensive damage and costly repairs. A proactive approach, along with expert knowledge, keeps your property safe from termites.



