The Types of Flies And Root Causes of Fly Infestations
May 20, 2025
The Hornets Nest, An In-Depth Look at Their Structure
May 26, 2025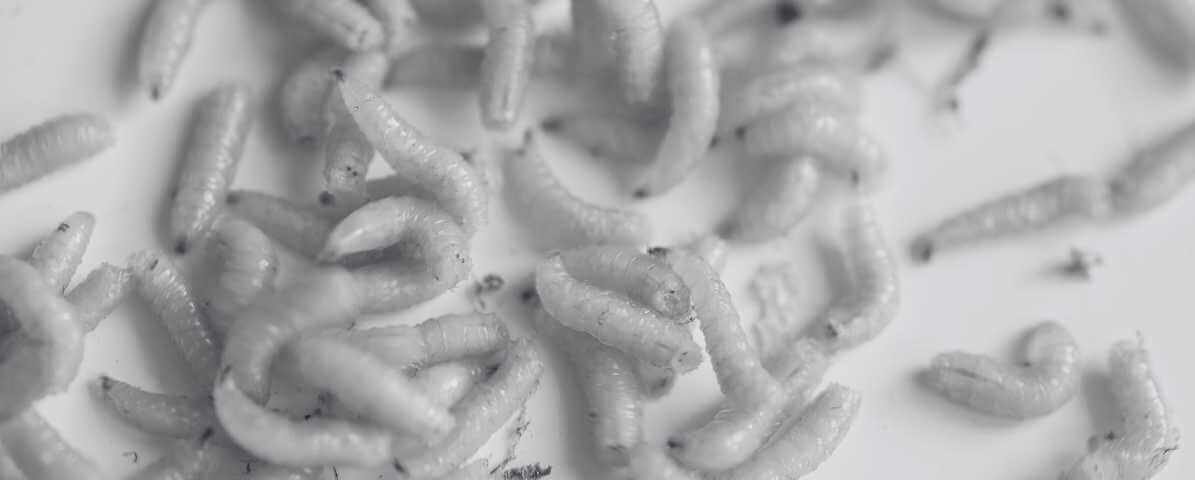
Flies Blog
A thorough understanding of the complete life cycle of a fly. Highlights how quickly a small problem can multiply into a large fly infestation.
The Complete Guide to Fly Life Stages
Understanding the Life Cycle of a Fly, From Egg to Adult
In Malaysia, where warm and humid weather creates ideal conditions for flies. Understanding the complete life cycle of a fly is essential for effective pest control. Flies are not only nuisances but can also pose health risks by spreading diseases. Knowing each stage, from eggs to adult flies helps in identifying infestation sources and implementing targeted management strategies.
We explores the fly's life cycle in detail, highlighting how environmental factors influence development. Offering practical tips to prevent fly infestations.
Understanding the Life Cycle of a Fly: From Egg, Fly Larvae to Adults
Overview of the Life Cycle of A Fly
The fly life cycle encompasses four primary stages: egg, larva (or maggot), pupa, and adult fly. Each stage varies in duration and environmental needs. But together, they form a rapid reproductive process that can lead to large numbers of flies if not controlled.
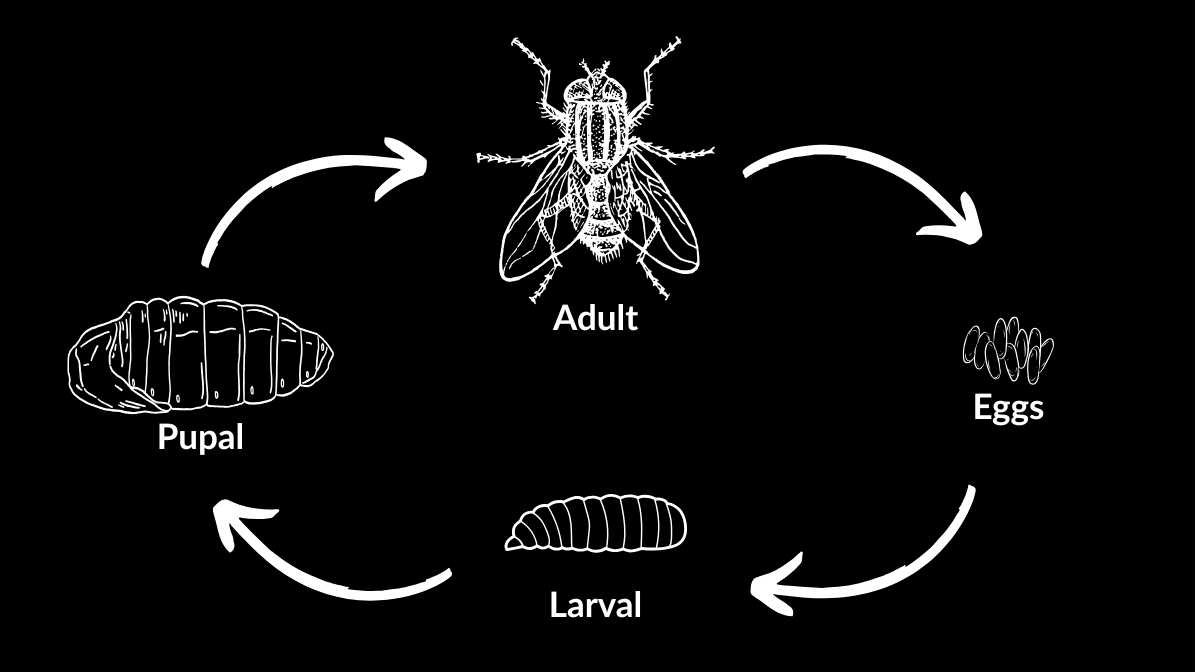
The Life Cycle of A Fly: How Fly Eggs Hatch and Develop
1. Egg Stage: The Beginning of Fly Life
The life cycle of a fly begins with the fly eggs, they breed in organic material rich in nutrients. Fly eggs are tiny, about 1.2 mm long, white or transparent, and oval-shaped. A female fly can lay hundreds of eggs during her lifetime, typically in clusters. Such as garbage, decaying food or animal faeces.
Different fly species prefer specific food sources:
The house flies eggs are usually in decomposing organic waste, such as food scraps and faeces.
Fruit flies (Drosophila spp.) deposit eggs on fermenting fruits and vegetables.
Other species, like drain flies, lay eggs in organic buildup inside plumbing.
The Life Cycle of A Fly: Fly Maggots and Larvae
2. Larval Stage: The Development of Fly Maggots
Once fly eggs hatch, the next phase is the larval stage, commonly called fly maggots. These legless, soft-bodied larvae feed intensively on the surrounding organic material, growing rapidly. Fly maggots typically remain in the larval stage for 24 hours to several days. In warm climates like Malaysia, this process is shorter, leading to quick population increases.
The egg, larva, pupa and adult phases are crucial for the development of new pest populations.
The larva can range from 3 to 20 mm long depending on the species.
During this stage, larvae develop in their food source. With environmental factors like temperature and humidity significantly influence their growth rate.
The Life Cycle of A Fly: Preventing Fly Infestation in Malaysia
3. Pupal Stage: The Transformation
Temperature and humidity are vital, warmer conditions accelerate the pupa development. In moist and warm Malaysian environments, the pupal phase tends to be shorter, leading to faster reproduction cycles. After enough feeding, larvae burrow into the organic material or soil and form pupae. The pupa is a hardened shell, usually about 4-9 mm long, where the transformation into an adult fly occurs.
The pupa stage can last from 3 days to several weeks depending on environmental conditions.
During this period, the insect undergoes metamorphosis, transforming from larva to adult.
The Complete Guide to Fly Life Stages
4. From Pupa to Adult Fly: The Final Stage The Life Cycle of A Fly
The final step in the life cycle is emergence of the adult fly from the pupa. The adult flies are ready to mate and lay eggs, which perpetuates the cycle. Fly species like house flies are notorious for urban environments, whereas fruit flies thrive where fermenting produce is present. Making proper garbage disposal critical for control.
Adult flies typically emerge in less than 24 hours after pupation.
They can live for 15 to 30 days, during which they reproduce prolifically.
Adult flies are highly adaptable and are commonly around food sources, garbage or places with organic debris.
How Can Proper Sanitation Help Prevent Health Issues Like Intestinal Myiasis Caused by Fly Maggots?
Fly maggots may causes intestinal myiasis in rare cases if contaminated food is ingest. Proper sanitation, therefore, is vital to prevent such health issues.
Managing Fly Infestations Effectively
The Significance of Each Life Cycle Of A Fly Stages
Understanding each stage's importance can help in crafting effective pest control strategies:
Egg Stage
Since flies lay their eggs directly in food sources or organic material. Removing or decontaminating these breeding grounds can prevent the initial part of the cycle.
Larval Stage (Fly Maggots)
This is the most destructive and visible stage, often involving large maggot infestations in garbage, drains, or decaying matter. Eliminating larvae by proper sanitation is crucial.
Pupal Stage
Still hidden in soil or organic matter. Making physical removal or environmental management essential to prevent adult flies from emerging.
Adult Stage
Responsible for reproduction; controlling adult flies with traps, screens, or insecticides can help break the cycle.
Identifying and Controlling Fly Infestation
Managing and Preventing Fly Infestation
Understanding the life cycle of a fly reveals critical control points:
Sanitation
Regularly clean all food sources and garbage disposal areas. Use tight seal lid trash bins and remove waste promptly.
Remove Breeding Sites
Discard decaying organic material, clean drains, and eliminate standing water to prevent fly eggs from hatching.
Control Food Sources
Keep fruits, vegetables, and open foods covered to prevent flies from laying eggs.
Physical Barriers
Install fine mesh screens on windows and doors to prevent entry of adult flies.
Fly Traps and Insecticides
Use baited traps or residual insecticides targeted at adult flies to reduce the population.
Biological and Environment Management Strategies
From Egg to Adult Pest Control in Malaysia
- Biological control methods like parasitic wasps can help in outdoor breeding sites.
- Maintaining proper garbage disposal and hygiene practices reduces organic material that flies and fly maggots depend on.
Professional Fly Control Services
Innovative Pest Blog Summary
Understanding the complete life cycle of a fly is fundamental to effectively controlling and preventing infestations. Since flies can quickly develop from eggs to adult flies within a week, prompt and consistent action is essential. Combining proper sanitation, secure barriers, and targeted pest control measures. Not only stops the reproductive cycle but also safeguards your health and hygiene.
Owners are encourage to remain vigilant, eliminate breeding sites like garbage and standing water. Seeking our professional pest control services when needed. By being proactive, you can keep your space free of flies. This helps stop small problems from switching into a severe infestations.
Why Clients Choose Us
✔ Years of Experience in Malaysia & Singapore
Our dual-market presence strengthens our capabilities and enhances our understanding of pest patterns across climates.
✔ Proven Results Across a Wide Range of Cases
From minor infestations to complex structural infestations, our case studies showcase our technical accuracy and problem-solving skills.
✔ Eco Friendly Commitment
We prioritise materials and treatments that reduce environmental impact while maintaining maximum effectiveness.
✔ Professional Guidance on Pest Identification
Our specialists guide customers on identifying early warning signs. Especially for termites, bed bugs and rodents, ensuring quick and accurate response.
✔ Clear Communication and Honest Reporting
Every treatment comes with documentation, service reports and preventive recommendations.
✔ Long-Term Protection Strategies
Our focus is not only to fix pest issues today, but to protect your space for the future.




