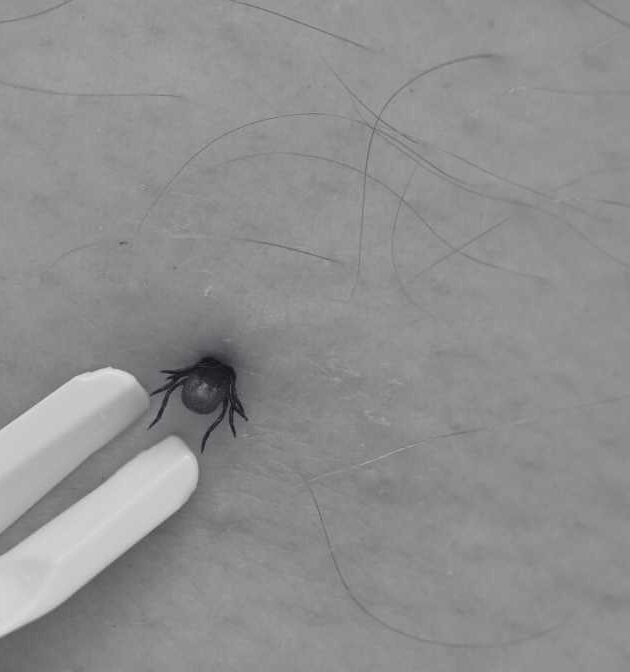
Learn More About Bed Bug Bites
July 15, 2024
Dengue Mosquito Cases (Nyamuk Aedes) Increase by 65%
July 24, 2024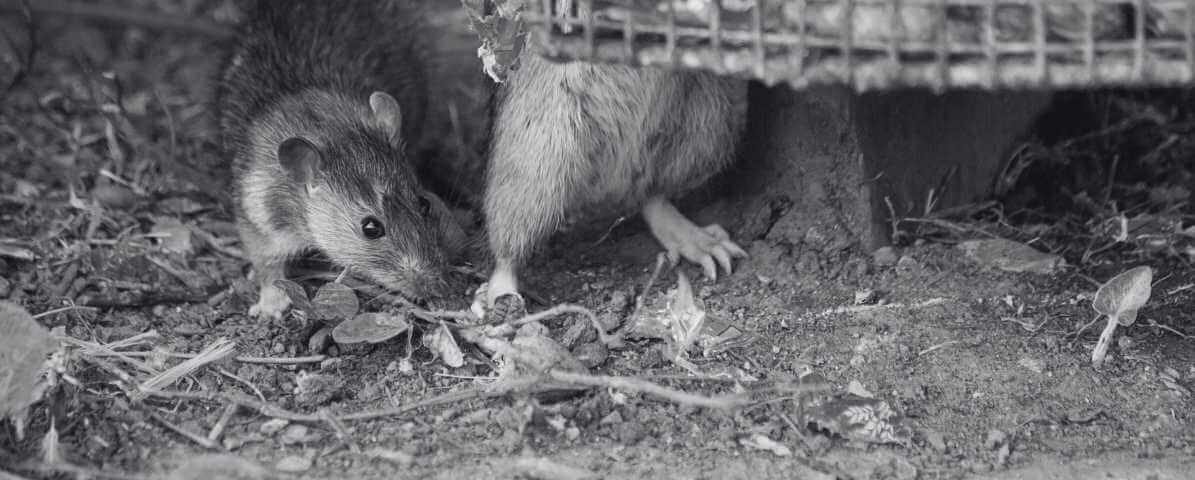
6 Dangerous Types of Diseases Rats and Mice Spread
Important to understand the different types of diseases spread by rats and mice. Many of these diseases can cause serious health problems. If no treatment is perform early, they can even be deadly.
The Hidden Threat of Rodent Diseases
6 Dangerous Types of Diseases Rats and Mice Spread
Rodents like the Norway rat, house mouse and other types of rodent are common in many parts of Malaysia. They often invade homes, especially if there is a rodent infestation, or they can live outdoors in areas with lots of food or shelter. Most people don’t realise it, rats and mice can carry infectious diseases that can make humans sick. The scary part is that many of these diseases spread through bites or scratches, food or drinks or even just handling a rodent.
We will cover six types of rodent diseases, explaining how they spread, the signs and symptoms. And most importantly, how to prevent these illnesses from spreading. Protecting yourself means understanding the risks, keeping your environment clean and practicing good hygiene.
Understanding the Different Types of Diseases Spread by Rats and Mice
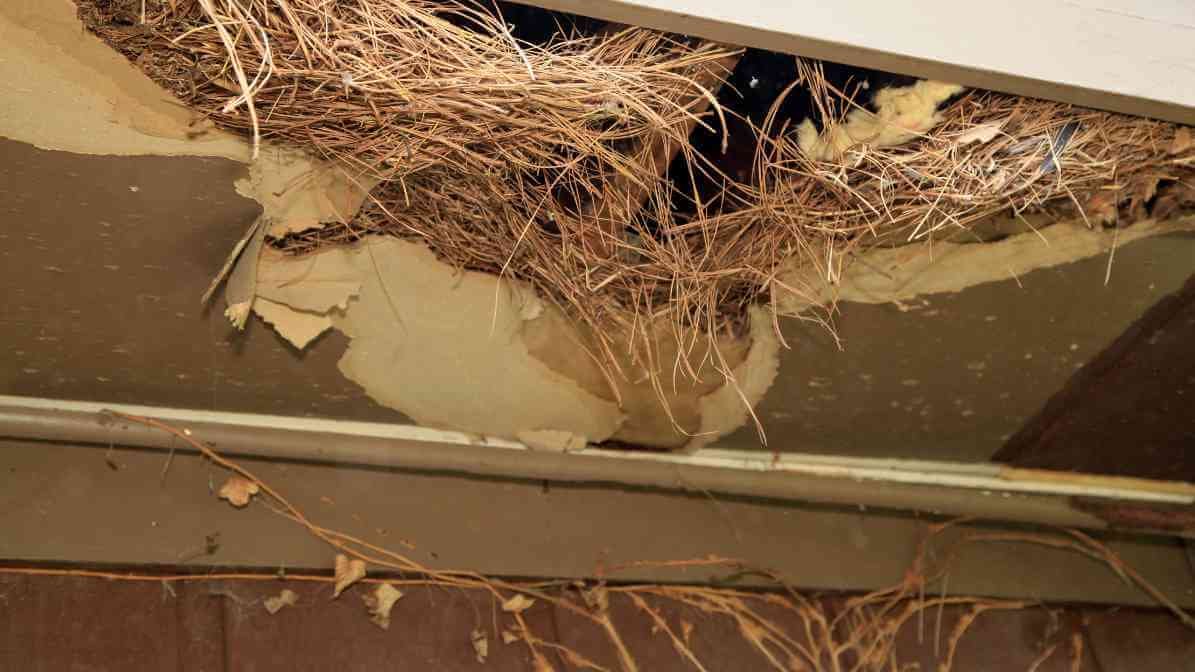
1. Hantavirus
Deadly infectious disease, mainly spread by wild rodents in residential and forest areas especially deer mouse and house mouse. These rodents spread it through their urine, droppings, saliva or nesting material. People usually get Hantavirus when they breathe in dust contaminated with rodent waste and urine. It happens when cleaning out areas where rodents have nest or when disturbing rodent droppings during a rodent infestation.
The infection usually develops within 1 to 5 weeks after exposure. Early symptoms include fever, muscle aches, dizziness and chills. As the disease progresses, it can cause severe lung problems, making it hard to breathe, which can be life-threatening. People might also experience headaches and nausea.



Facts and statistics:
In the United States, outbreaks of Hantavirus are rare but can be deadly. The CDC reports around 30-50 cases annually. Most cases happen in rural areas with rodent infestations. Especially during the fall and winter when mice seek shelter indoors.
Avoid sweeping or vacuuming their nests, instead use damp cloths and wear gloves.
Seal holes and cracks around your home to prevent rodents from entering.
Keep food sealed in containers and clean up crumbs or spills immediately.
Set traps or call pest control to manage a rodent infestation.
Do not disturb rodent nesting areas to reduce inhalation of contaminated dust.
Top 6 Types of Diseases Caused by Infected Rodents Around the World
2. Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus (LCMV)
A virus primarily spread by the house mouse, although uncommon than other rodent diseases, it can cause serious illness. Most infections happen when humans contact an infected rodent’s saliva, urine, droppings or nesting materials. Transmission can occur through bites or scratches from an infected rodent or contact with contaminated food or drinks. House mice at pet stores or in homes can get infect, making it a concern for pet owners too.
People infected with LCMV might just get mild flu-like symptoms like fever, muscle aches and fatigue. In some cases, especially in pregnant women, it can cause serious complications. Such as meningitis or encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain.



Interesting facts:
Person-to-person transmission of LCMV is rare., however, outbreaks can happen when infected rodents or their waste are shared. This can also occur through contact with contaminated surfaces. Cases are relatively rare, but they can be severe, especially in pregnant women or people with weakened immune systems. The CDC notes that most infections come from contact with infected rodents in homes or pet environments.
Practice proper hygiene around pet or wild rodents.
Handle pet rats or mice carefully, especially if they come from a pet store.
To clean up their waste, use a damp cloths and wear protective gloves.
Repair holes in the walls and keep rodents out of your property.
Store food securely and avoid leaving food or drinks open.
The Science Behind the Types of Diseases Transmitted by Pet Rats and Mice
3. Plague
Many people see the plague as a disease from medieval times, however, it still exists today. Bacteria spread by fleas that lives on rodents, particularly rats like the Norway rat. The bacteria are transmit when fleas bite an infected rodent and then bite humans. In some cases, direct contact with infected animals like handling an infected rodent can also spread the bacteria.
In rare cases, the bacteria can enter the body through cuts or bites or even inhalation of infected droplets. The most common form of plague causes swollen, painful lymph nodes called buboes. Symptoms include fever, chills, weakness and muscle aches. If untreated, the bacteria can spread to the lungs (pneumonic plague), which makes breathing difficult and can be fatal.



Interesting facts:
The plague is rare but still present in some parts of Malaysia. The CDC reports around 10-20 cases annually in the United States. With most cases occurring in rural or semi-rural areas with a high rodent population.
Keep your home and yard clean to prevent rodent and flea infestations.
Seal holes in the walls where rodents might be able to enter.
Use pest control to reduce rodent populations.
Avoid handling wild rodents or their carcasses.
Use flea control products on pets and around your home.
How Urban Rodent Infestations Contribute to Different Types of Diseases in Cities?
4. Salmonella
Salmonella is a bacteria that causes food poisoning. Many rodent diseases, including Salmonella, spread through the contamination of food or drinks. Often because of getting in contact with rodent droppings or urine. Infected rodents like pet rats or wild mice can leave bacteria in their droppings.
If the droppings or urine touch surfaces, food, or drinks, people can get sick from consuming them. Cross-contamination often happens in kitchens or food storage areas where rodent activity is present. Symptoms include diarrhoea, stomach cramps, fever and vomiting. It usually develops within 6 hours to 6 days after exposure and can last up to a week.
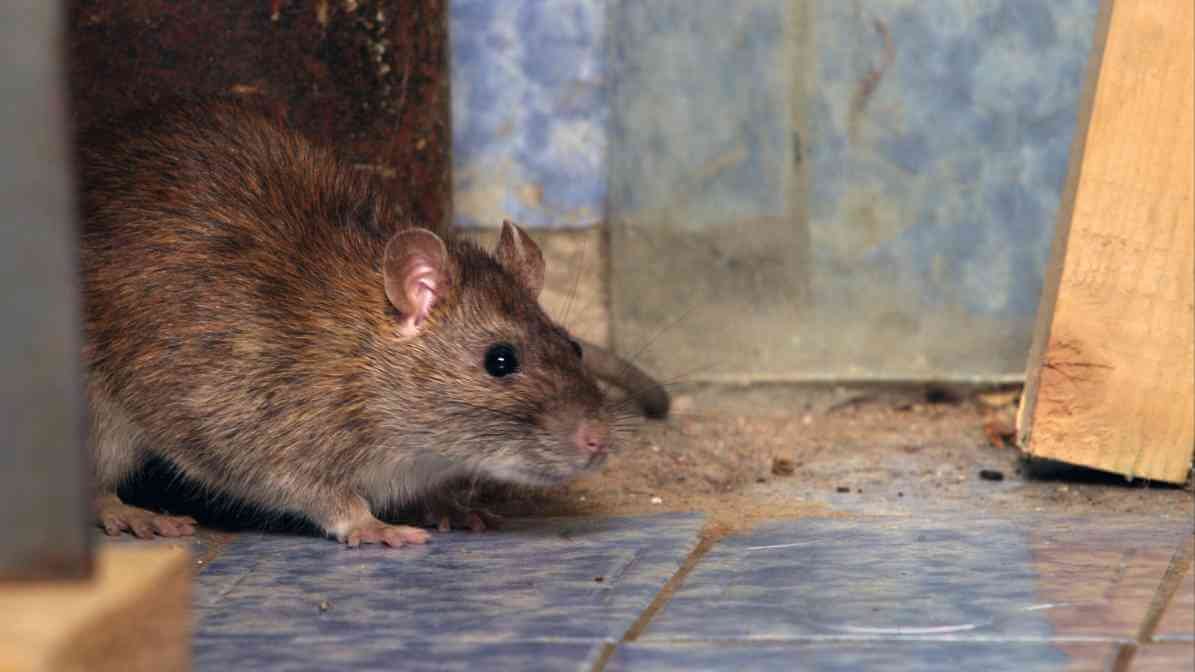



Interesting facts:
In Malaysia, reports have emerged about Salmonella outbreaks linked to pet rats and rodents in pet stores. Proper hygiene and pest control are vital to prevent contaminated food or drinks.
Keep food stored in sealed containers.
Clean areas where rodents have been with disinfectant.
Regularly inspect your home for signs of rodent infestation.
Properly dispose of rodent waste using gloves and disinfectant.
Maintain good hygiene and wash hands thoroughly.
The Connection Between Rodent Infestations and the Spread of Types of Diseases in North America
5. Rat Bite Fever (RBF)
A bacteria that infect rodents, particularly rats and mice, transmission of bacteria are through bites or scratches. Bacterial infection that can make humans extremely ill if bitten or scratched by infected animals. Most cases happen when a person gets bite or scratch by an infected rodent, such as wild rats or pet rats from a pet store. Handling infected animals or contact with their urine or droppings can also increase risk.
Sometimes, even minor bites or scratches can lead to infection if bacteria enter the skin. Within 3 to 10 days of a bite or scratch, symptoms include fever, rash, joint pain and swelling at the site of the bite. If not treated promptly with antibiotics, the infection can become serious.
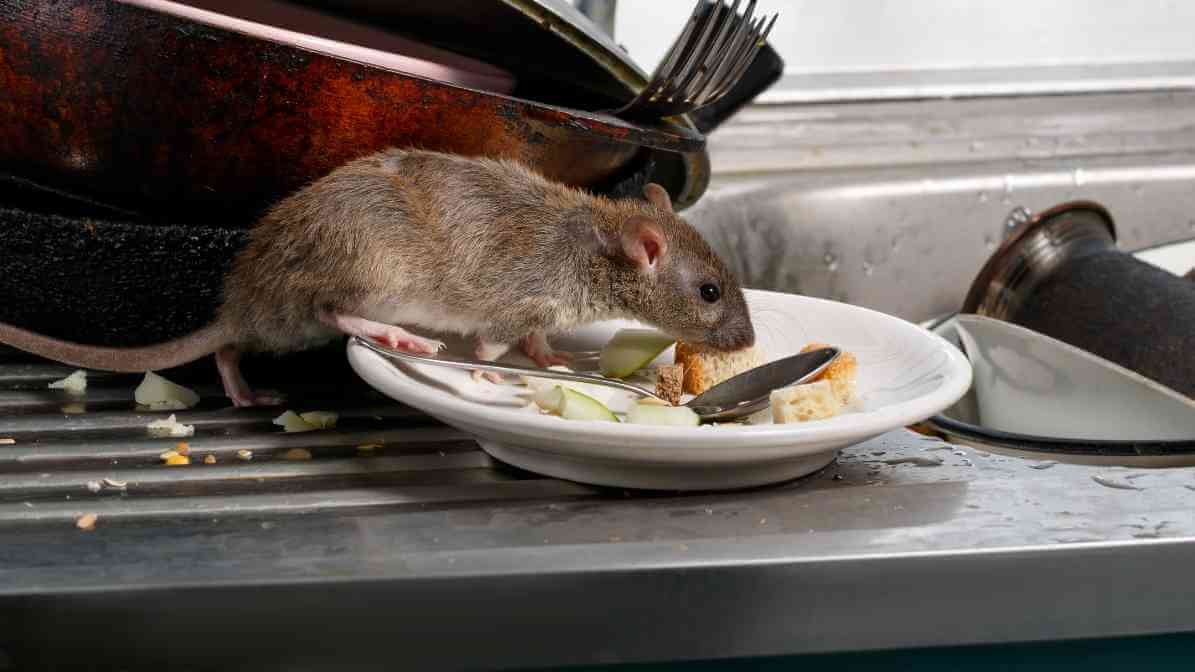

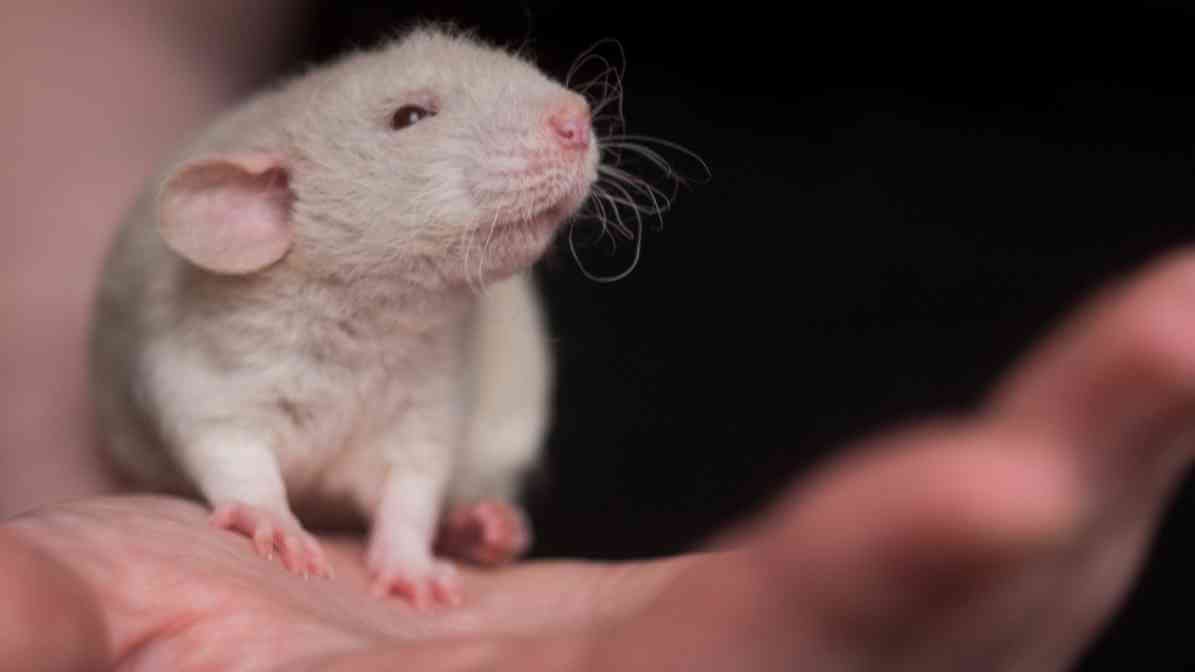

Fun fact:
The disease name, rat bite fever (RBF), is a reminder of how important it is to be cautious after bites or scratches from rodents.
Handle pet rats and mice carefully, ideally wearing gloves.
Watch for signs of infection after a bite or scratch and seek medical attention.
Keep rodents in a clean environment to prevent infection.
Avoid handling wild rodents or their droppings.
Preventing the Spread of Different Types of Diseases through Pest Control Measures
6. Tularemia
Tularemia is a bacterial disease caused by Francisella tularensis. Sometimes people address it as “rabbit fever” and rodents, including mice and rats, spread it. Tularemia spreads mainly through bites from infected rodents or ticks that have fed on infected animals. Can also be contract when handling infected rodents directly or through contact with contaminated food or water.
When a rodent dies and its blood or tissue contaminates food or drinks, people who eat or drink those items can get sick. The symptoms vary depending on how the person was infect, but common signs include fever, skin ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, sore throat and chills. In some cases, causing pneumonia and difficulty breathing if inhale during cleaning activities.



Relevance to Malaysia:
Although tularemia is relatively rare, it still occurs in certain parts of the region. The CDC reports occasional outbreaks, especially during the summer months when rodents and ticks are most active. Pest control and proper hygiene are key to reducing risk and avoiding serious illness.
Use Innovative pest control professionals to prevent rodent infestation around your home. Especially if you live in areas with a high wild rodent population.
Wear gloves and protective clothing when handling rodents or cleaning up rodent droppings.
Cover food and water sources to avoid contamination.
Avoid handling dead rodents or their carcasses without proper safety measures.
What Should I Do If A Rat Bites or Scratch Me?
Clean the wound immediately with soap and water, apply disinfectant and seek medical attention. A doctor may recommend antibiotics or other treatments, especially if symptoms develop.
The Role of Rodent Control in Reducing Different Types of Diseases in Communities
Why Is It Important to Know About The Types of Diseases?
Wild rodents carries infectious diseases without showing signs of illness, they appear healthy and transmit dangerous bacteria or viruses. For pet owners, it’s equally important to be cautious. Pet rats from a pet store might carry some of these diseases if they are infected animals. To keep your pet rats healthy, handle them carefully and maintain good hygiene to prevent diseases like rat bite fever.
In communities with rodent infestation, controlling pests is one of the most effective ways to prevent disease transmission. Sealing entry points, setting traps and working with our pest control professionals will significantly reduce rodent-borne illnesses. In rat reproduction, 21 days is usually the age at rat pups are wean. The young rats are typically separate from their mother and begin to eat solid food on their own.
Signs and Symptoms of Common Types of Diseases Carried by Rodents
How Can You Protect Yourself and Your Family?
Keep your home, especially kitchens and food storage areas, clean and free of food scraps or spills that attract rodents.
Seal Entry Points
Block holes in walls, doors, and windows to prevent rats and mice from entering the house.
Manage Food Wisely
Store food in sealed containers and avoid leaving drinks or food out in open areas.
Control Rodent Populations
Use traps or call pest control when you notice signs of rodent infestation like droppings or gnaw marks.
Handle Rodents Carefully
If you own pet rats, make sure they come from reputable sources like a pet store and handle them gently with clean hands or gloves.
Be Cautious After Bites or Scratches
If bitten or scratched by a rodent, clean the wound immediately with soap and disinfectant, then seek medical attention.
Disinfect Thoroughly
Clean areas contaminated with rodent waste using disinfectant and wear protective gear.
Professional Rodent Control Services
Innovative Pest Blog Summary
Wild rats and mice are more than just pests, they carry serious diseases. Including Hantavirus, Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis Virus (LCMV), plague, Salmonella, rat bite fever (RBF) and tularemia. These diseases including some that can be transmit through bites, scratches, contaminated food or drinks. Or contact with infected animals poses a real threat, especially during rodent infestation problems in homes and communities.
Good news is that most of these diseases can be prevent with responsible pet ownership, good hygiene and pest control measures. When cleaning areas with rodent activity, wearing gloves and practicing safety precautions helps reduce the risk of infection. Remember, awareness is your best tool in preventing rodent-borne illnesses. Stay cautious, stay safe, and don’t hesitate to seek professional help if you notice signs of a rodent infestation.
Why Clients Choose Us
✔ Years of Experience in Malaysia & Singapore
Our dual-market presence strengthens our capabilities and enhances our understanding of pest patterns across climates.
✔ Proven Results Across a Wide Range of Cases
From minor infestations to complex structural infestations, our case studies showcase our technical accuracy and problem-solving skills.
✔ Eco Friendly Commitment
We prioritise materials and treatments that reduce environmental impact while maintaining maximum effectiveness.
✔ Professional Guidance on Pest Identification
Our specialists guide customers on identifying early warning signs. Especially for termites, bed bugs and rodents, ensuring quick and accurate response.
✔ Clear Communication and Honest Reporting
Every treatment comes with documentation, service reports and preventive recommendations.
✔ Long-Term Protection Strategies
Our focus is not only to fix pest issues today, but to protect your space for the future.




